Revolutionary Applications of DensePose From WiFi: Enhancing Corporate Security and Empowering Military Tactical Teams
 Cutting-edge technologies continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in the realm of wireless communication and security applications. It seems like every week there is something new in the technology front that enhances our capabilities in the security world. Most notably since the revelation of ChatGPT, almost everything recently seems to be “AI” (artificial intelligence) based technology. Cornell University’s groundbreaking research on DensePose From WiFi has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how we perceive and utilize Wi-Fi signals. This article delves into the potential implications of that technology in corporate security for occupancy and muster reporting, as well as exploring its potential for portable deployment variations for military and tactical teams to visualize assailants through walls and barriers.
Cutting-edge technologies continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in the realm of wireless communication and security applications. It seems like every week there is something new in the technology front that enhances our capabilities in the security world. Most notably since the revelation of ChatGPT, almost everything recently seems to be “AI” (artificial intelligence) based technology. Cornell University’s groundbreaking research on DensePose From WiFi has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how we perceive and utilize Wi-Fi signals. This article delves into the potential implications of that technology in corporate security for occupancy and muster reporting, as well as exploring its potential for portable deployment variations for military and tactical teams to visualize assailants through walls and barriers.
Understanding DensePose From WiFi (DensePose WiFi)
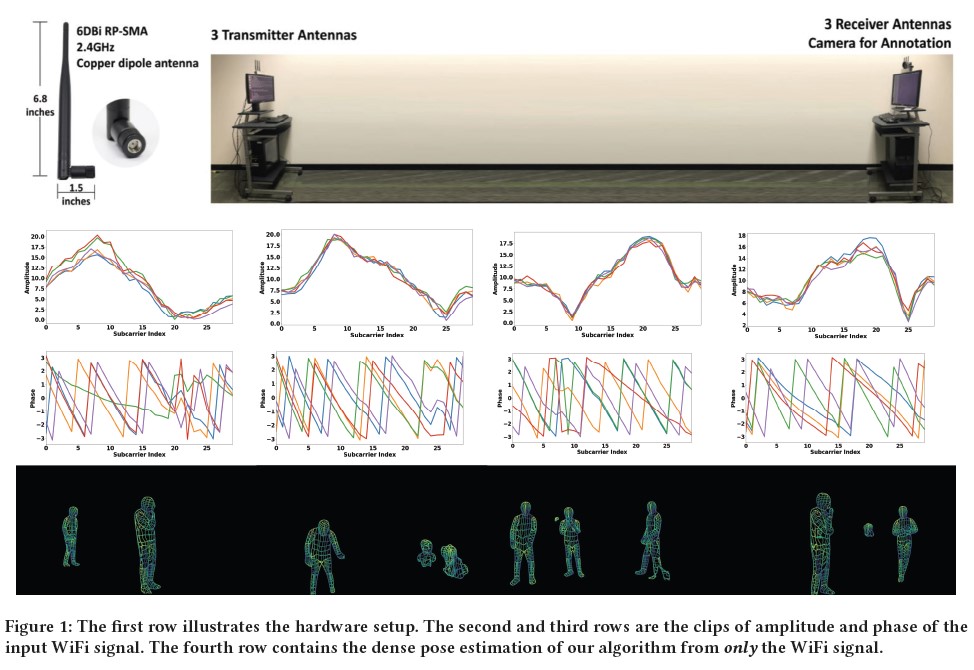
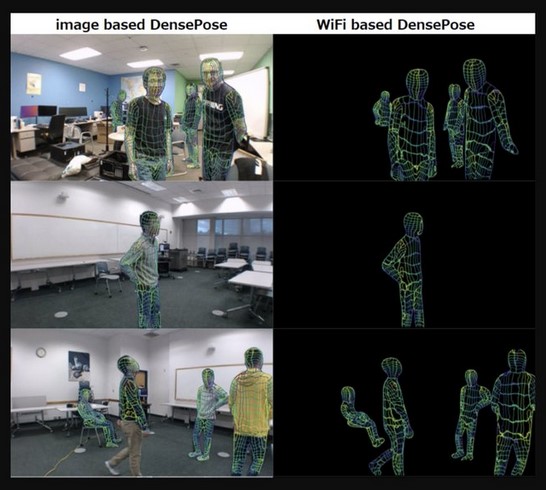
DensePose From WiFi is a pioneering research project that harnesses the power of radio frequency (RF) signals to track and analyze human movements in a given area. The technology leverages the existing Wi-Fi infrastructure and transforms it into a sophisticated motion-capture system. By analyzing the reflections and refractions of Wi-Fi signals as they interact with the human body, DensePose can generate accurate 3D representations of people’s movements in real-time. The technology is based off of previous research (called simply DensePose) that utilizes video images with deep learning networks to correlate video camera imaging data to map the estimations of human body poses within its field of view. DensePose’s objective is to provide human pose estimation that aims at mapping all human pixels of an RGB image to the 3D surface of the human body. DensePose From WiFi took the video technology, paired it with WiFi data to feed into an AI deep learning model, and then took away the camera feed. The result is an imaging capability just using radio waves. Think of it as a type of bat sonar, except using signals from WiFi routers that can see further, and potentially through walls and other objects.
Corporate Security: Occupancy and Muster Reporting
One of the most promising beneficial applications of DensePose WiFi lies in enhancing corporate security measures, particularly in the realm of occupancy and muster reporting. Traditional methods of monitoring people’s presence within a building rely on physical sensors such as In/Out card readers, AI cameras, mustering point check-in readers, or even manual headcounts, which can be time-consuming and prone to inaccuracies, especially with visitors. However, with DensePose WiFi, businesses can now leverage their existing Wi-Fi infrastructure to precisely track and report the occupancy of various spaces to determine if a space, or even an entire floor, are “all clear”. An entire building could be scanned within seconds to determine if the building is clear, and if not, provide security or first responders with the floor and exact location where those remaining individuals are.
When integrated with an intelligent security system, DensePose WiFi can monitor the flow of employees throughout a building, ensuring that everyone is accounted for in case of emergencies or evacuation drills. This technology enables real-time muster reporting, providing an accurate headcount and identifying any areas that may require immediate attention during critical situations.
Other potential applications could include patient wandering systems for hospitals, vacancy verification, or even automatic threat assessment alarms generated by certain poses which represent an obvious threat (gun aiming posture, headlock, standing over another person, etc).
Enhancing Security for Military Tactical Teams
The potential applications of DensePose WiFi extend beyond corporate settings and can prove to be invaluable for military tactical teams. In scenarios where situational awareness is crucial, such as hostage rescue missions or urban combat, this technology can be a game-changer.
By outfitting military personnel with lightweight and portable (or perhaps weapon mounted with heads-up display) Wi-Fi like transceivers, tactical teams can effectively “see” through walls or other obstructions. DensePose WiFi would allow operators to detect and track the movements of individuals on the other side of barriers, providing vital intelligence before initiating any tactical actions. This enhanced situational awareness could save lives and offer a considerable advantage in complex and high-stakes operations.
Ethical Considerations and Privacy Concerns
While DensePose WiFi presents tremendous potential for improving security measures, it also raises ethical and privacy concerns. The technology’s ability to generate 3D representations of human movements demands a delicate balance between security and individual privacy. Striking this balance will be crucial for ensuring public acceptance and responsible deployment of this technology in various domains.
DensePose WiFi represents an exciting leap forward in the realms of security and wireless communication. Its applications in corporate security for occupancy and muster reporting promise increased efficiency and safety in emergencies, while its potential use in military tactical scenarios offers unprecedented situational awareness. As this technology continues to evolve, it is essential to address ethical considerations and privacy concerns to foster its responsible adoption and ensure a secure and ethical future for all.