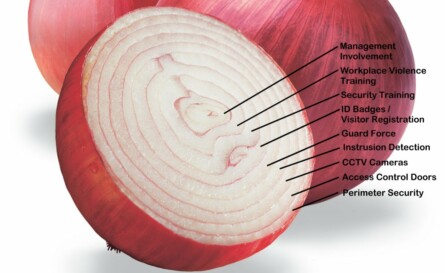
The Importance of Security Consultants in Designing Effective Security Systems
In an ever-evolving world with increasing security concerns, it has become imperative for businesses and organizations to prioritize the implementation of robust security systems. However, choosing the right approach and ensuring an effective security setup is not always straightforward. A renewed trend that was prevalent a couple of decades ago was for integrators to offer “consulting and design services’. Often, businesses rely on security integrators to design and install their security systems, and for certain size projects that makes sense. Why hire an outside consultant to design a small retrofit project? While security integrators play a crucial role, there are significant benefits to involving a security consultant in the design process. In this article, we will explore the virtues of using a security consultant and highlight examples of where security installers have fallen short or encountered conflicts of interest.
- Unbiased Expertise: A security consultant brings a unique perspective and unbiased expertise to the table. Unlike security integrators who are often affiliated with specific brands or manufacturers, security consultants have a broader understanding of the security landscape and can offer impartial advice. Their experience in assessing risks and designing comprehensive security strategies ensures that the resulting system is tailored to the specific needs of the organization. We don’t sell or install anything, and thus have no particular preference for what products the client may choose to consider for their project. That doesn’t mean we won’t make recommendations about their requested choices (see our past articles about our strong feelings on putting corporate security data in the cloud or using NDAA banned products). The short version: if your consultant receives remuneration from a manufacturer or vendor for the products they specify, find another consultant.
- Conflict of Interest: One of the key concerns when relying solely on security integrators is the potential for conflicts of interest. Integrators may be motivated to prioritize their own profit margins or partner relationships over the best interests of the client. This can lead to compromised system designs, subpar equipment selection, or inadequate coverage. You may be sold a particular brand or product line because there is a sales goal incentive being pushed by management or the manufacturer. Worse, it is not uncommon for integrators to unload poor selling product or superseded parts in order to clean up their inventory. This is fine if the client is aware and accepts the product (presumably for a discount), but sometimes it is done without their knowledge. By involving a security consultant, businesses can mitigate these conflicts and ensure that their security system is designed with their unique requirements in mind.
- Prevent Poor Project Management: Integrators will often bake in “project management” and “system check out” line item fees in their proposals, claiming to offer project management and punch list services for their own installation phase. This is very much like having the fox watch the hen-house. In one recent case, we saw a project where a vendor substituted the installed camera
models with inferior (cheaper) models AFTER they received the bid award and purchase order. The client didn’t catch it, but we did during project field inspections. Never let the integrator perform their own punch list and acceptance testing.
- Post Installation Documentation: Trying to get as-built documentation is often another problem. While almost nobody likes doing as-built drawings, their value should never be underestimated. Ask anyone who has done a retrofit project without them. If the client does not hold back a percentage of payment until all punch list items are complete and all as-built documentation is submitted, then the likelihood of that work ever being done without further consideration can be very low. Too, often the integrator will simply take the original design drawings and update them slightly (or not at all) and turn them in as the as-built documentation. That is insufficient. Good as-built documents include the original equipment list (mfr/model, qty, serial #s, IP addresses, power, etc) and locations, riser diagrams, installation details, as well as the point-to-point wiring and configuration details for every piece of installed equipment. If the vendor uses a tool like System Surveyor or Fieldwire, ask for the full report to be printed to PDF and included in the as-built documentation. (You may also want to request they delete the data being stored on the cloud if your organization has data retention policies that concern this situation).
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Security consultants conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas of concern. This includes evaluating physical vulnerabilities, assessing technological risks, and analyzing procedural weaknesses. By considering these factors during the design phase, consultants can develop an integrated security system that addresses identified risks, ultimately providing greater protection against potential threats. This may include out-of-scope items that may not be viable under the current project funding, but can be provided to the client so the cost can be projected under future budgets or other projects which can resolve the issue.
- Future-Proofing: Security systems should be adaptable and scalable to meet evolving security requirements. Integrators might focus solely on immediate needs, potentially overlooking future expansion or technological advancements that may be outside the scope of their work or capabilities. Security consultants, however, take a holistic approach by considering the long-term goals and growth plans of the organization. This ensures that the security system is flexible and can accommodate future upgrades or changes without significant disruptions or additional costs.
While security definitely integrators play a critical role in the installation of security systems, involving a security consultant during the design and project management phases offers numerous advantages. Their unbiased expertise, ability to identify vulnerabilities, and focus on long-term planning can significantly enhance the effectiveness of a security system. By avoiding conflicts of interest and addressing potential pitfalls, businesses can ensure a comprehensive and robust security solution tailored to their specific needs.
Remember, investing in the services of a security consultant is an investment in the long-term safety and security of your organization. Don’t leave the design of your security system to chance—seek the guidance of an expert to achieve the peace of mind you deserve.








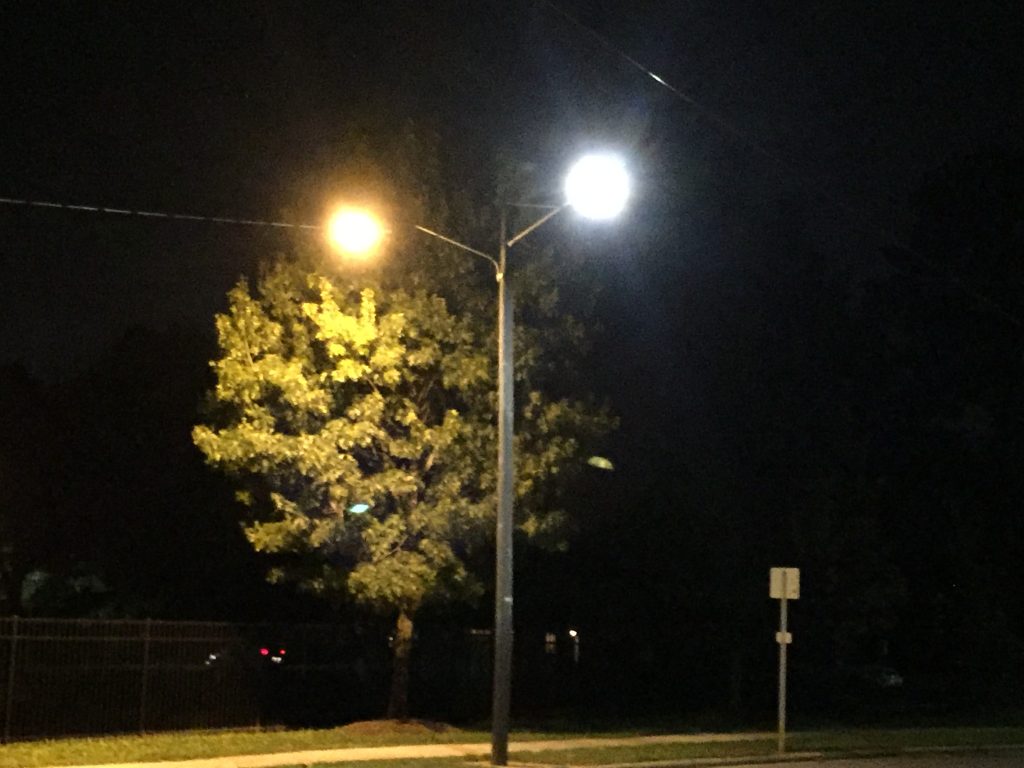
 old, yellow street lights now shine bright white and bright with the latest in modern street lights, LEDs. LED lights are popular because of their tremendous energy savings, about 80-90% energy efficiency, when compared to a traditional incandescent light bulb. This means the LED lamp has about 80% of the energy used to illuminate actually goes into making the light, with the remaining 20% given off as thermal energy. Compared with the highly inefficient incandescent bulb, which is about 25% converted to light, and 75% given off as heat. So for any business, residence, or municipality, a huge savings in operating costs can be found by switching to LED lighting, and with federal subsidies for energy savings, the capital costs are partially offset as well.
old, yellow street lights now shine bright white and bright with the latest in modern street lights, LEDs. LED lights are popular because of their tremendous energy savings, about 80-90% energy efficiency, when compared to a traditional incandescent light bulb. This means the LED lamp has about 80% of the energy used to illuminate actually goes into making the light, with the remaining 20% given off as thermal energy. Compared with the highly inefficient incandescent bulb, which is about 25% converted to light, and 75% given off as heat. So for any business, residence, or municipality, a huge savings in operating costs can be found by switching to LED lighting, and with federal subsidies for energy savings, the capital costs are partially offset as well.